Have you ever wondered how metal parts for things like cars, appliances, and electronics are made?
Well, one of the ways is a process called die casting.
Die casting is a cost-effective manufacturing process used to create high-quality and complex metal parts with tight tolerances and excellent surface finishes.
The process itself is particularly useful for businesses looking to manufacture custom metal components intended for specific industrial applications.
The following sections will cover everything you need to know about the die casting process.
We’ll go over everything from the different types of die castings to the alloys and die used, the steps involved in the process and the different surface finish options that are available.
This guide aims to give you a better understanding of the process so that you can decide whether or not it is a good fit for your manufacturing projects.
In die casting, molten metal is inserted into a die or mold with the use of an injection system, and left to cool. As it solidifies while cooling, it takes on the shape of the mold.
This method is primarily used to produce parts with high accuracy and consistency.
The history of die casting dates back to the mid-1800s when the first patent for a die-casting machine was filed in the United States.
These early machines were manually operated, and the dies were made of iron or brass.
The development of hydraulic and electric machines in the 1940s and 1950s improved the speed and accuracy of the process, making it more efficient and cost-effective.
Die casting has come a long way since then, and today it has become an exclusively automated process.
Modern die-casting machines use computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) technology to create highly complex parts.
The importance of die casting to manufacturing and engineering processes cannot be overstated.
It has allowed manufacturers to create intricate shapes quickly and accurately.
As manufacturing technology continues to advance, so too will the process of die casting and its capabilities.
There are two main types of die casting: hot chamber die casting and cold chamber die casting.
Let’s take a closer look at each one to better understand the differences between them.
Hot chamber die casting is used for metals with low melting points, such as magnesium, tin, and lead.
During this process, the injection system, consisting of a piston and a sleeve, is submerged in molten metal, which is held in a furnace attached to the machine.

Once the piston is pushed, the molten metal is injected into the die and allowed to solidify.
The process is quick and efficient, which is why it is such a popular choice when high-volume production is needed.
In contrast to the hot variety, cold chamber die casting is used for metals with high melting points, like aluminum, copper, and zinc.
In this process, the molten metal is first poured into a separate chamber (i.e., the cold chamber that gives the process its name), and only then is it injected into the die.
As with the hot chamber process, the cold chamber injection system consists of a piston and a sleeve.
The piston and sleeve never come into contact with the molten metal.
Instead, a metal ladle is used to transfer the molten metal from the furnace to the cold chamber.
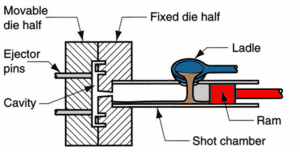
It should be noted that cold chamber die casting takes longer than hot chamber die casting.
This is because metals with high melting points cannot be melted in the injection system alone and, therefore, must be transferred to the cold chamber to be completely formed.
In summary, hot chamber die casting is a quick and efficient manufacturing process that is used for low-melting point metals.
Cold chamber die casting, on the other hand, is used for high-melting-point metals and takes longer to complete since these types of metals tend to form at a much slower rate.
Dies play a crucial role in shaping the metal into the desired form during the die casting process.
The quality of the dies significantly impacts product quality, production cycle time, and overall cost-effectiveness of the process.
There are four main types of dies used in die casting:
You can see a schematic depiction of what each type looks like in the image below.
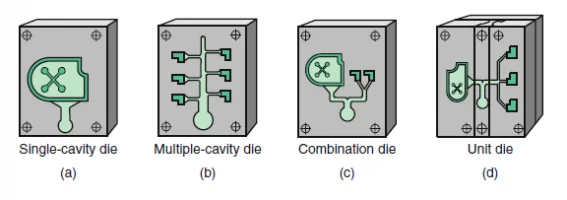
Let’s take a closer look at each one.
Single cavity dies are the simplest type of dies and are used for producing a single part or unit at a time.
Using a single cavity die is by far the most time-consuming and expensive way to cast parts in a die, as each part must be created individually.
Single cavity dies are good options for small batch productions and for parts that require complex geometries.
Multiple cavity dies can produce multiple identical parts at the same time.
Naturally, they are more cost-effective than single cavity dies.
These dies are suitable for producing large quantities of simple parts in a single go.
Combination dies are used when multiple parts with different shapes and sizes need to be produced.
These dies have multiple cavities that allow for the creation of different parts.
Combination dies tend to be more efficient than single cavity dies and even regular multiple cavity dies, as they allow for the production of multiple different parts in one cycle.
Unit dies are similar to combination dies. Both kinds are designed with extreme precision to ensure accuracy in the final product.
However, unit dies have a fixed shape and size, while combination dies are custom-made to fit the specific needs of the customer.
Unit dies are used for producing large quantities of simple parts, making them a cost-effective option for high-volume production.
Understanding the different types of dies used in die casting is important if you want to choose the best option for your specific purposes.
In die casting, the type of alloy used strongly determines the quality and durability of the finished product.
Out of the many alloys used in manufacturing today, the following are the most commonly used in die casting:
Let’s take a closer look at each one.
Aluminum alloys are the most widely used alloys in die casting.
This is primarily due to their excellent strength-to-weight ratio, high corrosion resistance, and good mechanical properties.
Aluminum alloys are ideal for producing lightweight parts for the automotive, aerospace, and electronics industries.
Bronze alloys are used to produce parts with superior hardness, strength, and wear resistance.
They are one of the most suitable materials for producing bearings, gears, and other machine components.
Lead alloys are used for their low melting point, excellent machinability, and flexible formidability.
They are also able to withstand high temperatures without losing strength or durability.
Because of all this, these alloys are ideal for producing small, intricate items such as bullets and fishing weights.
Magnesium alloys have an excellent strength-to-weight ratio, are corrosion-resistant, and are lightweight.
Thus, they are a perfect fit for cast parts used in the aerospace and automotive industries.
Tin alloys are used when corrosion resistance and good mechanical properties are needed.
Their high threshold to wear and tear also allows them to be used in electronic components like electrolytic capacitors,
Zinc alloys can be easily cast into intricate shapes with thin walls, sharp corners, and complex geometries.
They are usually chosen for applications commonly used in the automotive and electronics industries due to their good thermal conductivity.
Understanding the unique properties of each alloy used in die casting is key to ensuring the highest quality and durability of the finished product.
The die casting process involves five steps. Each of them plays an important role in ensuring the final product meets its required specifications.
The following is a detailed overview of the steps.
The first step begins with cleaning and lubricating the die before it is clamped and closed under high pressure.
Clamping ensures that the die is securely sealed and the molten metal doesn’t leak out during the casting process.
Once the die is clamped, the metal is melted and poured into the shot chamber.
The molten metal is then forced into the die cavity under high pressure, which makes it take the shape of the mold.
The molten metal must be injected at the right temperature, speed, and pressure to achieve optimal results.
While still clamped, the metal is allowed to cool down and solidify into the shape of the mold design.
The cooling process can be accelerated by circulating a coolant (i.e., water or oil) through the die.
After the metal has cooled, the die is unclamped, and the ejection mechanism (ejector pin) is allowed to push the casting out of the die.
The injection pins help mitigate any damage to the casting while it is removed from the die.
In the final step, excess metal is removed from the finished product using a trimming tool or saw.
Trimming makes sure that the casting meets the required dimensions and specifications of the finished product.
Each of the steps listed above requires specialized knowledge and skill, as well as high-end equipment and materials, in order for the castings to come out according to specification.
Surface finishing can add tremendous value to the products that are the result of die casting. The benefits include aesthetic appeal, corrosion resistance, and improved tensile strength.
There are a variety of surface finishing options available for die casting. Let’s look at the most popular ones.
Painting is a frequently used finishing option that adds color and durability to components that are the product of die casting.
It is quite cost-effective and simple in its application. All you need to do is paint the casting and allow it to dry.
Different types of paints can be used depending on the intended use of the product.
Powder coating is another popular finishing option that provides a durable and long-lasting finish.
The process involves applying a dry powder to the surface of the part produced via die casting, and baking it to create a hard finish.
This type of finish can be used for most metals that operate in harsh environments as it provides durability, resistance to chipping and scratching, and protects against corrosion.
This type of surface finish is used to create an aged and weathered appearance on the parts produced with the use of die casting.
The weathered appearance is achieved by using chemicals or sandblasting to remove the top layers of the surface material.
While antiquing is commonly used in home decor, it can also be applied in construction, for purposes such as building exteriors, particularly brickwork and stonework for historic homes or buildings.
Ceramic coating involves applying a ceramic material (e.g., a liquid polymer) to the surface of the part produced through die casting.
This coating is resistant to wear and tear, while at the same time providing a high-quality, aesthetically-pleasing finish to the product.
These coatings are most commonly used in the automotive industry. They protect against scratches and minor dings and add shine and gloss to a vehicle’s paintwork.
Plating is another surface finishing method that involves applying a thin layer of metal to the surface of the die-casting part.
This finishing process can be accomplished using various metals, like gold, silver, and copper.
The primary purpose of plating is to improve the appearance and durability of an object, while also providing additional resistance against corrosion, wear and tear, and other environmental factors.
It’s commonly employed when the underlying material cannot provide sufficient protection or desirable aesthetic qualities (e.g., the chrome finish on car parts).
There are several surface finishing options available for die casting.
The choice of the finishing option will depend on the intended use of the product, the desired appearance, and the functional properties required.
Die casting is an effective and cost-effective manufacturing process that can be used to produce complex and high-quality metal parts for various industries.
Both types of die casting processes (hot chamber and cold chamber die casting) employ different types of dies and alloys to produce complex shapes with thin walls.
Such a result would be difficult or impossible to achieve using other manufacturing methods.
Die casting is the process of choice for applications where lightweight yet strong components need to be manufactured at high volumes and in a cost-effective manner.
Various surface finish options can also be employed during die casting to enhance the appearance and texture of the finished product.
Additionally, the finished product is also more resistant to wear and tear, as well as corrosion.
Since there are many moving parts to the die casting process, it’s important to consult with a custom metal manufacturer like Bunty to assess its suitability for your project.
From a contract manufacturing firm, BuntyLLC evolved into a full service custom machined, forged and cast metal parts fabrication enterprise. We supply global solutions from our headquarters in Greenville, South Carolina.
Get A Quote